Importance of First Aid for Outdoor Survival
Having first aid knowledge saves lives during outdoor activities. Emergencies arise unexpectedly when hiking, camping, or exploring remote areas. Understanding how to handle injuries like cuts, burns, and sprains ensures immediate response, reducing complications.
Quick intervention minimizes long-term damage. Basic first aid skills stabilize an injured person until professional help arrives. For example, knowing how to clean and dress a wound prevents infection.
First aid boosts confidence during outdoor adventures. When prepared, you handle emergencies calmly and effectively. This mental preparedness enhances the overall outdoor experience, making it safer and more enjoyable.
Preparedness is key. Carrying a first aid kit and knowing how to use its contents gives you the tools to treat injuries on the spot. Essential items include bandages, antiseptics, and pain relievers. Having these supplies readily accessible allows for prompt treatment.
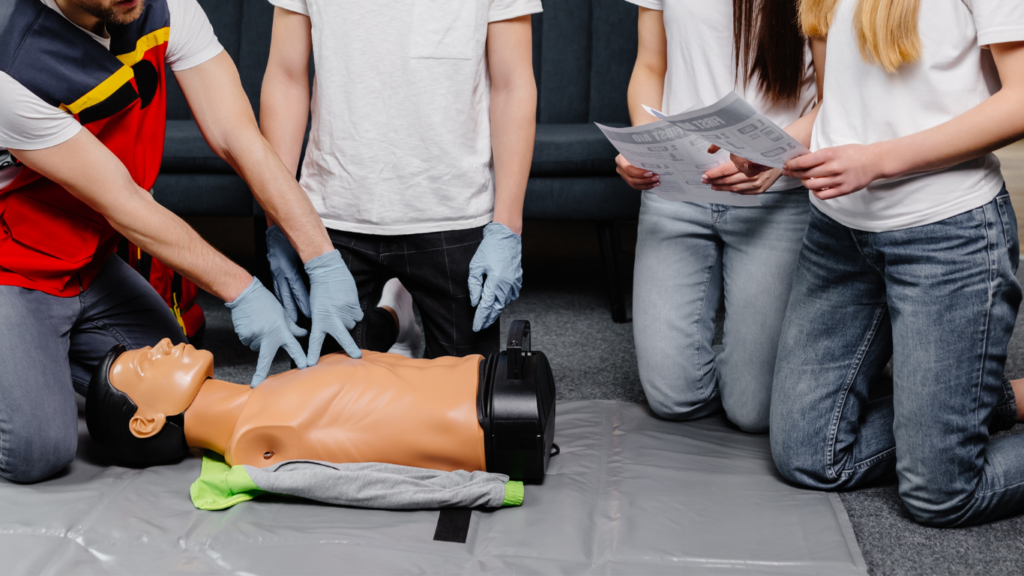
Training improves safety. Enrolling in a first aid course provides hands-on experience on managing outdoor injuries. Practical knowledge from such courses reinforces theoretical understanding, building a solid foundation for effective first aid application in the field.
Overall, first aid skills are crucial for outdoor survival. In emergencies, they transform a potentially dire situation into a manageable one, ensuring safety and peace of mind during outdoor adventures.
Essential First Aid Skills

Having the right first aid skills can make a difference during outdoor adventures. Below, you’ll find essential techniques to manage emergencies effectively.
Assessing the Situation
Accurately assessing the situation is vital. First, ensure the safety of everyone at the scene. Next, check the injured person’s condition by looking for consciousness, breathing, and any visible injuries. If severe, contact emergency services.
CPR and Rescue Breathing
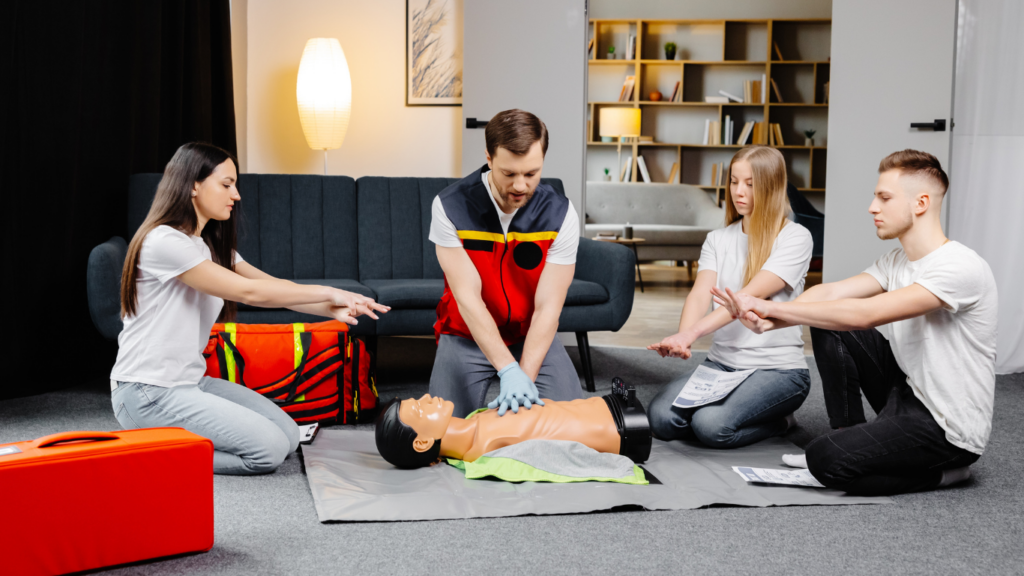
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) and rescue breathing can save lives. Begin by placing the heel of your hand on the center of the person’s chest and interlock your fingers. Perform 30 chest compressions at a depth of 2 inches, followed by two rescue breaths. Continue until help arrives.
Wound Care and Bandaging
Proper wound care prevents infections. First, clean cuts with water or antiseptic wipes. Apply pressure to stop bleeding, then use sterile bandages to cover the wound. For burns, cool the area under running water for at least 10 minutes and cover with a non-stick sterile dressing.
Fracture and Sprain Management
When handling fractures and sprains, immobilize the affected area. Use a splint to stabilize fractures, ensuring not to move the injured limb unnecessarily. For sprains, follow the RICE method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
Hypothermia and Heat Exhaustion Treatment
To treat hypothermia, first remove wet clothing and wrap the person in dry, warm blankets. Offer warm, non-alcoholic drinks slowly. For heat exhaustion, move the person to a shaded area, provide cool water, and apply wet cloths to lower body temperature.
Utilizing these first aid skills can significantly impact survival and safety during outdoor activities.
First Aid Kit Essentials
Having a well-stocked first aid kit for outdoor activities ensures you’re prepared for any emergencies.
Must-Have Items
Certain items are non-negotiable when it comes to a first aid kit for outdoor survival. These essential components allow for immediate intervention in case of injuries or medical issues.
- Bandages and Gauze: Variety of sizes for dressing wounds and controlling bleeding. For example, adhesive bandages for small cuts and sterile gauze pads for larger wounds.
- Antiseptic Wipes and Solution: Clean wounds to prevent infection. Antiseptic wipes sanitize the wound area, while solutions like hydrogen peroxide help with deeper cleaning.
- Medical Tape: Secure dressings and immobilize splints. Effective for keeping gauze in place and supporting sprains.
- Pain Relievers: Medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain management. Helpful for headaches, muscle pain, and minor injuries.
- Tweezers and Scissors: Remove splinters, debris, and trim medical tape or bandages. Precision tools for delicate tasks.
- Emergency Blanket: Provide thermal insulation to prevent hypothermia. Essential in cold environments and for treating shock.
- CPR Mask: Perform rescue breathing safely. Barrier protection during CPR to prevent cross-contamination.
- Instant Cold Packs: Reduce swelling and relieve pain for sprains and strains. Activated by squeezing to provide cold therapy on the go.
- Gloves: Protect both the injured person and the caregiver. Use disposable latex or nitrile gloves to maintain hygiene.
- First Aid Manual: Step-by-step instructions for various medical emergencies. A quick reference guide for effective response.
Optional Additions
While the essentials cover the basics, additional items can enhance your first aid kit’s functionality, targeting specific needs and personal preferences.
- Aloe Vera Gel: Soothe burns and sunburns. Useful for managing minor skin injuries.
- Antihistamines: Treat allergic reactions. Vital for those prone to allergies or insect bites.
- Burn Cream: Apply to minor burns for pain relief and faster healing. Contains ingredients to cool and protect the skin.
- Electrolyte Tablets: Prevent dehydration and replenish lost minerals. Handy for long hikes and hot weather.
- Snake Bite Kit: Treat snake bites in remote areas. Includes suction devices and instructions for initial care.
- Eye Wash Solution: Flush out debris or chemicals from the eyes. A sterile solution for eye-related emergencies.
- Hydrocortisone Cream: Relieve itching and inflammation from insect bites or plant contact. Reduces discomfort from skin irritations.
- Flexi Splints: Stabilize fractures or severe sprains. Lightweight and versatile for immobilizing injured limbs.
- Pediatric Supplies: Tailor the kit for children if they’re part of the group. Smaller bandages and specific medications for kids.
- Signal Whistle: Attract attention in an emergency. Useful for rescue situations to alert others.
Training and Practice
Training and practice are key to effectively using first aid skills in outdoor emergencies. Acquiring proper knowledge through courses and regularly practicing these skills ensures readiness.
Finding a First Aid Course
Finding a first aid course doesn’t need to be complicated. Many organizations, such as the American Red Cross, offer courses tailored to outdoor emergencies. You can search their websites for available classes. Local community centers and health organizations also provide training sessions. Check their schedules for upcoming classes. Be sure to choose a course that covers CPR, wound care, and injury management. Verify that the course includes hands-on practice to enhance skill retention.
Practicing Skills Regularly
Practicing skills regularly is essential to maintain proficiency. Set aside time each month to review and practice your first aid techniques. Use training dummies or practice with friends to simulate real-life scenarios. Focus on CPR, bandaging wounds, and treating burns. Rotate through different scenarios to ensure broad preparedness. Practice helps reinforce muscle memory, making it easier to perform under pressure. Keep your knowledge updated by attending refresher courses or advanced training sessions annually.
Tips for Staying Safe Outdoors
Staying safe outdoors requires planning and awareness. I focus on several key strategies to ensure my safety and well-being during outdoor activities.
1. Plan Ahead
Research and understand the area you’ll visit, checking weather conditions and terrain. Prepare for changes in weather by packing appropriate clothing and gear.
2. Carry Essential Gear
Always bring essential equipment like maps, compasses, and a fully charged phone. Carry multiple navigation tools in case one fails.
3. Stay Hydrated
Bring enough water for the duration of the trip. Consider water purification methods like tablets or filters if you plan to stay longer.
4. Monitor Health
Watch for signs of dehydration and heat exhaustion. Symptoms like dizziness and nausea require immediate attention.
5. Be Aware of Wildlife
Know the types of wildlife in the area and how to react if encountered. Store food securely to avoid attracting animals.
6. Inform Others of Your Plans
Let someone know your itinerary and expected return time. This step ensures help can be dispatched if you’re overdue.
7. Learn Emergency Skills
Basic knowledge like building a shelter and signaling for help can be lifesaving. Practice these skills regularly.
8. Follow Trail Markings
Stick to marked trails to avoid getting lost. Unauthorized paths can lead to unsafe areas.
9. Wear Appropriate Footwear
Choose sturdy footwear to protect your feet and prevent injuries. Footwear with good traction reduces the risk of slips.
10. Carry a First Aid Kit
A well-stocked first aid kit is crucial. Include items like bandages, antiseptic wipes, and pain relievers.
11. Know the Signs of Hypothermia
Understanding symptoms like shivering and confusion helps in early detection and prompt treatment.
Using these strategies enhances safety and preparedness for outdoor adventures.